DDKJ - Mastering Soldering Iron Temperature Control: Ensuring Quality and Safety in Welding
DDKJ - Mastering Soldering Iron Temperature Control: Ensuring Quality and Safety in Welding
DDKJ - Mastering Soldering Iron Temperature Control: Ensuring Quality and Safety in Welding
Soldering is a crucial process in electronic manufacturing and repair, and mastering the correct temperature of the soldering iron is fundamental for achieving high-quality solder joints. Improper temperature control can not only affect product reliability but also cause component damage or safety issues.
This article will discuss how to control soldering iron temperature, the soldering temperature requirements for different materials and components, and the problems that can arise from excessive temperature.
1. How to Control Temperature
Proper temperature control begins with selecting the right tools and settings. A soldering iron with temperature adjustment capabilities is the ideal choice, allowing operators to adapt the temperature according to the different soldering materials and components. Additionally, the following points are also very important:
- Preheating: Ensure the soldering iron is fully preheated to the set temperature to guarantee stability when soldering begins.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the soldering iron's temperature settings to address any deviations, especially after extended use.
- Cleaning: Keep the soldering iron tip clean, as oxidation and contaminants can affect heat transfer efficiency.
- Monitoring: Regularly check the actual temperature using a thermal imager or a dedicated soldering iron temperature tester to ensure accuracy.
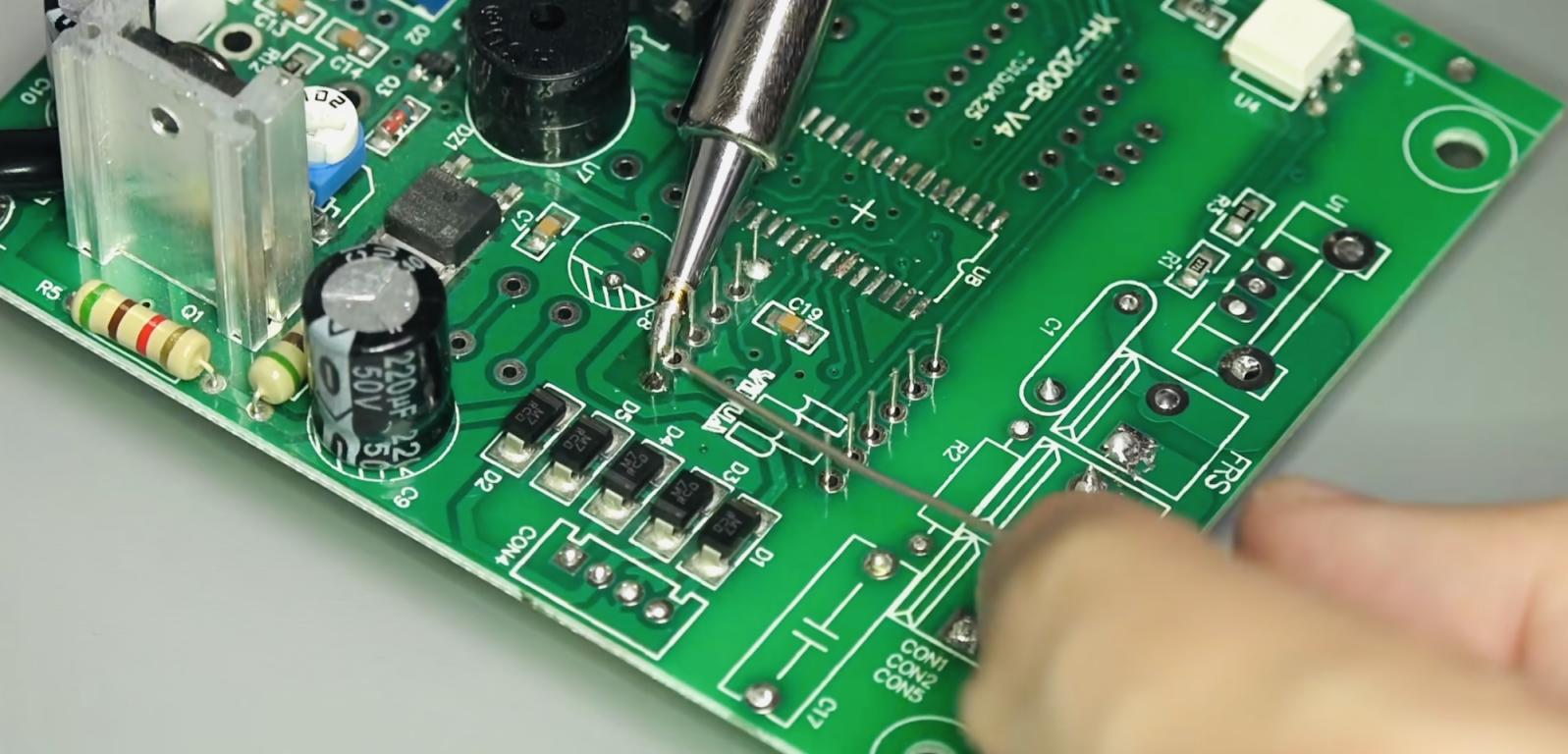
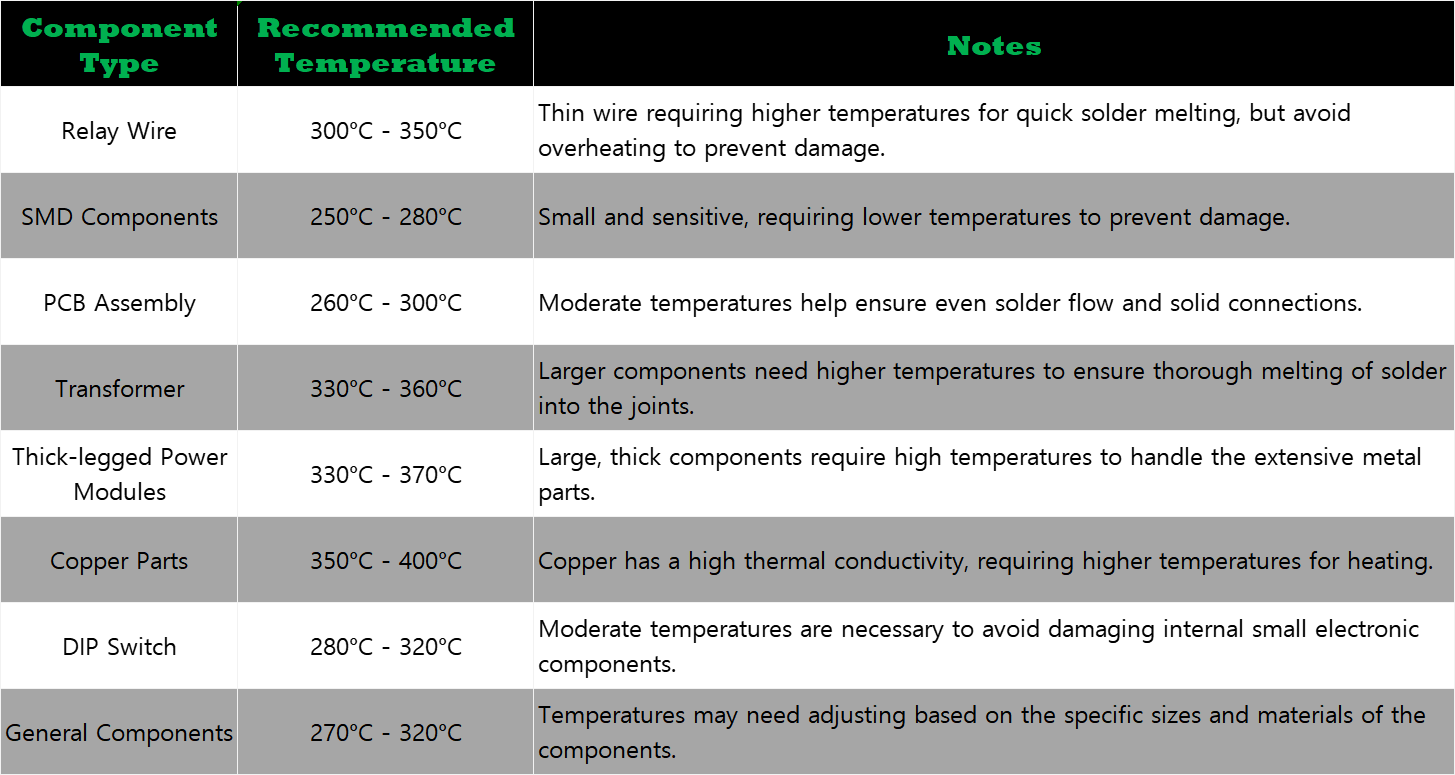
2. Soldering Temperature Requirements for Different Materials and Components
The table below lists the recommended temperature ranges for soldering various common materials and components:
3. Problems Caused by Excessive Temperature
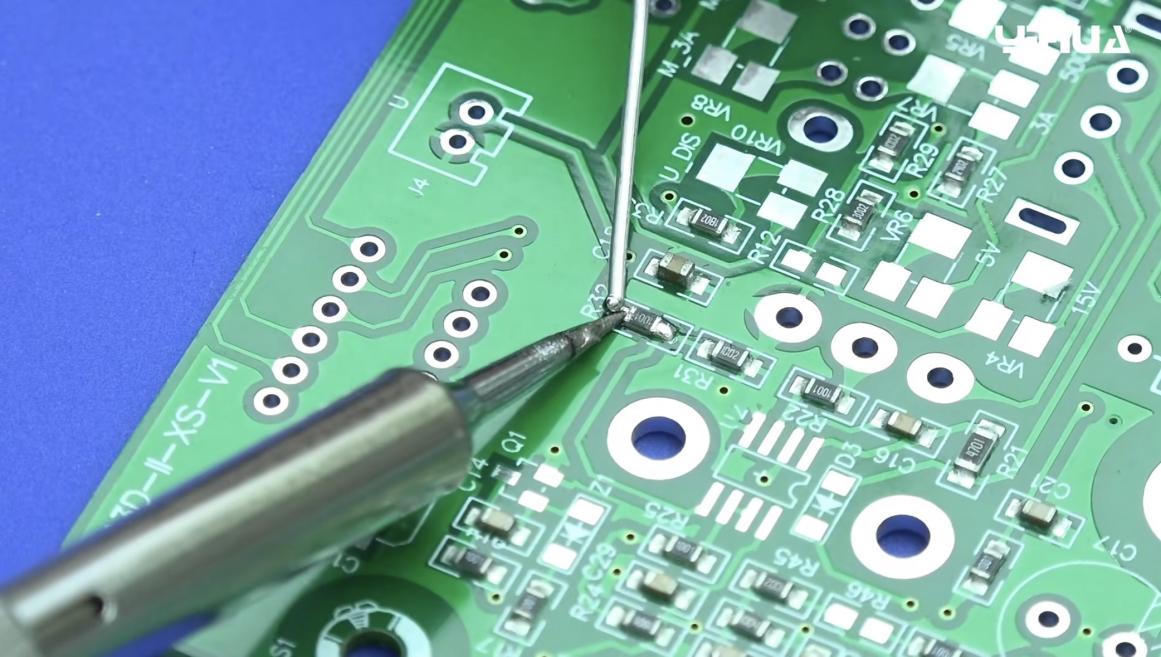
Setting the temperature too high can lead to a variety of problems that affect both the quality of the soldering and safety, including:
- Weak Solder Joints: Excessively high temperatures can cause solder to flow too much, resulting in cold solder joints.
- PCB Damage: High temperatures can cause thermal damage to PCB materials, such as delamination of copper layers or warping of the substrate.
- Component Damage: Sensitive electronic components can be damaged by high temperatures, affecting device functionality.
- Health Risks: Higher temperatures exacerbate the oxidation of solder and flux, increasing the release of harmful gases.
In conclusion, precise control of the soldering iron temperature is crucial for ensuring product quality and operational safety in soldering tasks. At Dadao Electric Co., Ltd. (DDKJ), we strictly control the temperature of the soldering iron, reducing quality issues from the source and protecting the safety of operators.
 English
English
How Do You Read a Water Meter
A water meter is an important tool that tracks the amount of water used in your home or business. Learning how to read it correctly not only helps you verify your water bill but also allows you to detect leaks, monitor consumption, and conserve resources more efficiently. Whether your property has a traditional mechanical meter or a modern digital one, understanding how to read a water meter is a straightforward process.
Read MoreHow to Check Water Meter
A water meter is an essential device that records how much water flows into your home or business. Regularly checking your water meter can help you monitor consumption, detect leaks early, and manage your water bills more effectively. Understanding how to check a water meter is a simple but valuable skill for every property owner or tenant.
Read MoreWhat Does a Water Meter Look Like
A water meter is a compact yet vital device designed to measure the amount of water consumed in homes, businesses, and industries. While many people know its purpose, fewer are familiar with what a water meter actually looks like and how its design varies depending on its application. Understanding its appearance and structure helps users recognize and maintain this essential tool more effectively.
Read More